After the change of administration in 1832, Thailand had have 2 important laws for land and construction tax which were Act of Property tax in 1832 and Act of Local maintenance tax in 1975, the latter still effectively valid until today. Various parts of Acts of tax are still problematic. Therefore; the government came up with an idea of improvement which is joining the two Acts as one and named it “Act of land and construction tax.” The idea of joining two Acts is also well spread in many reigns of previous governments. Whenever there is an attempt to get rid of any inequalities in the society, the idea of improving and joining two Acts and make it more effective with progressing rank taxation will become an issue. The idea that the change made to this law will increase the power to gather incomes and spread them to local areas; hence the locals gain more administrative power to govern people, duties, and expenditure also becomes a concern of the issue. Nonetheless, the idea always ends up as a lame prediction since every time the idea has been picked up then it has been protested from the disadvantaged benefiters, many previous governments then foldaway the project.
The situation goes the same with the government which rules after Coup d’état in 2014. This government also brings up the same issue to consideration and nearly pushes the Act to validate successfully. On March 9, 2015, Mr. Sommai Phasee; Minister of Ministry of Finance informed that the latest approach (before it was forced to slow down) announced the cancellation of all taxation exclusions which will be replaced by an indicated tax with low ranks in order to reduce burdens of low incomes people. Nevertheless, the base of taxation will become larger since everybody who has a property regardless of the property’s price will have to pay the land tax. Tax ratios are as follows.
For example, the owner of the house pays 250 baht tax for the house valued at lower than 1 million baht, pays 500 baht tax for the house valued at 2 million baht, pays 1,000 baht tax for the house valued at 3 million baht, pays 1,500 baht tax for the house valued at 4 million baht, pays 2,500 baht tax for the house valued at 5 million baht, pays 7,500 baht tax for the house valued at 10 million baht, and pays 17,500 baht tax for the house valued at 20 million baht. On the other hand, an agricultural land will be exempted from taxation if the land is valued at lower than 1.5 million baht.
After March 11, 2015, General Prayut Chan-ocha; Prime Minister and leader of National Council for Peace and Order has ordered the Ministry of Finance to slow down the Act of land and construction tax in which he reasoned the Act might cause problems for civilians from problematic economy. He has ordered to postpone the Act until 2017.
This part will look at several examples from 10 foreign countries that have the same type of taxation and how their taxation mechanism works.
Land and construction tax: Foreign experiences
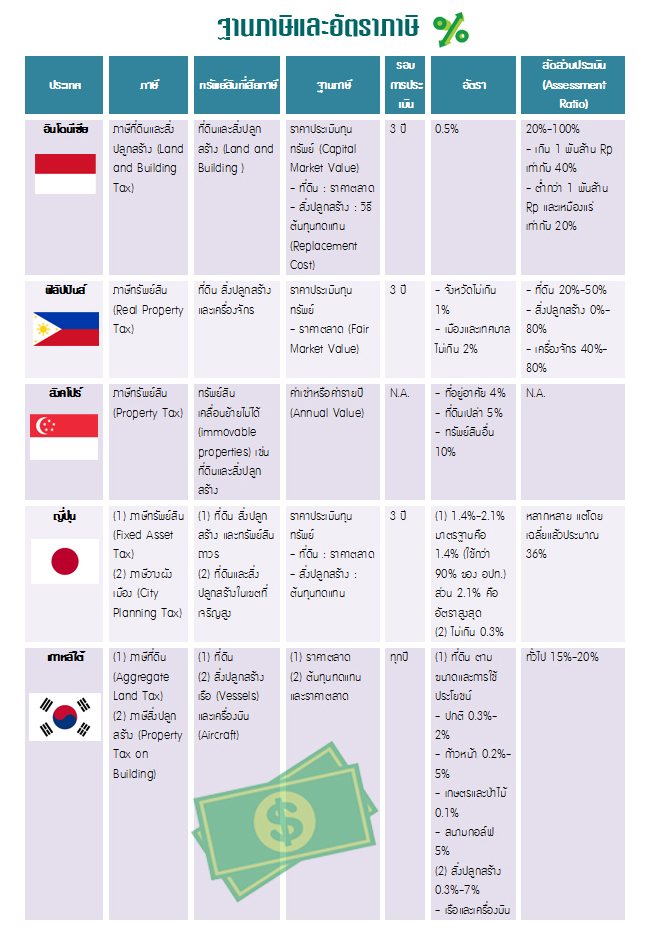
After the coup d’état took over Thaksin Shinawatra’s government in 2004, the issue of “land tax” was picked up again as a mechanism to reduce inequalities in the society. At that time, there was a systematic study from a research called “the consideration of draft of law about land and construction” in which the research was conducted by the Finance committee, the Bank, money institutions and National Legislative Assembly of 2007 which Mr. Sangsit Piriyarangsan was a chairman. The research compares property tax of 10 foreign countries including Australia, England, France, the United States of America, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Singapore. In the research there are various interesting topics that can be summarized as follows.
Go to 'จับตา' for “การจัดเก็บภาษีที่ดินและสิ่งปลูกสร้าง ของประเทศต่างๆ 10 ประเทศ”
Tax Base The research shows that most of the ten countries have land and construction taxation (both for personal and for commercial). There are some countries that have machinery taxation such as the Philippines and Japan. In South Korea, there are tax for boats and planes as well. Australia is the only country out of ten that have land taxation with construction taxation.
Property that needs no taxation In ten countries, they provide omission from taxation for some properties and the assessments differ from each country such as, the use of ownership (State or Public’s property, the use of utility (properties that are used for charity activities or non-profit activities) or the traits of the owners (elders or disabled, etc.) Most of the properties which have been exempted from tax are State’s properties, schools and universities’ properties, religious properties, public graveyards, public hospitals, charity and non-profit organizations, streets and public parks, libraries, embassies and properties of international organizations such as the United Nations. Moreover, in some countries there is an exclusion of tax for agricultural lands and houses as well.
Property value assessment For an assessment to evaluate property value to find the proper taxation, in most cases it is found that almost every country use Capital value as a tax base. Only Singapore and France use rents and annual rents as their tax bases as same as property tax in Thailand. The interesting point is that England is the only country that uses both assessments which are Council tax as a tax base for personal properties and Rent tax as a tax base for business properties.
The point which requires closer look is that most of the assessments for land value use a method in which market price is the main point of assessment. Contrary to construction value assessment, in which most of the 10 countries use a method of Replacement Cost which is a method of finding value of buildings which are considered as replacement of new buildings with similar materials and designs along with local labors, all of those will actually indicate the cost of the buildings. When the decay value is excluded, then there will be a current building value. In the United States of America, with progress of collecting data technology, they also use a method that include market price to find the value of buildings as well. For Australia; the country with only land tax uses a land assessment which is called “Unimproved Value of Land” in which they auction each land as if that land has never been developed.
Period of property value assessment Good and fair property tax depends on methods of most-likely-true-to-the-first-assessment property value assessment and apart from that, it also depends on periods of Revaluation or how often the assessments are. This is because a property value depends and differs with changeable conditions of economical and societal environment. Therefore, evaluate the property value frequently is the way to create a current price for the property and also prevent an overly increase of the property price that will cause tax payers to pay more and burden them with taxes. Yet, the frequent property value assessment may affect the increase of the state’s capital. Therefore; the property cannot be evaluate annually.
From the study, it is found that countries which have an annual property value assessment are South Korea, some states of Australia, and some states of the United States of America. Countries that have a property value assessment in every three years are Indonesia, the Philippines, Japan, and Taiwan. And countries that have a property value assessment in every five years or more than that are England, France, some states of Australia, and some states of the United States of America.
Organizations that are responsible for property value assessment In most cases, a federal government is the one responsible for this duty or at least they are the ones who designate rules and regulations for the property value assessment for Departments of Local Administration. Countries that federal governments are responsible for the property value assessment are England, France, Australia (State government), Indonesia, and Singapore. On the other hand, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and the Philippines let their local administrations handle the issue follow by the rules and regulations indicated by their federal governments. For the United States of America, the country combines both Departments of Local Administration and State governments in order to responsible for the property value assessment.
Tax Ratio The study shows that group of countries that use a market price as their tax base will have a tax ratio at around 0.3%-7%. Contrary to group of countries that use rent as their tax base will have a very diverse ratio of tax such as Singapore’ tax ratio is around 4%-10%, England’s tax ratio is around 42%-43.6%. For France, the country’s tax ratio depends on how much their Departments of Local Administration want to spend which cannot be over a rate the law has specified, this method from France goes the same with the United States of America.
However, truth be told that tax ratio specified in the law or Nominal Rate and tax that has been collected or Effective Rate are often different. For example, Indonesia has its nominal rate at 0.5% but its effective rate is less than 0.5%. The Philippines has its nominal rate at 2% but its effective rate is only at 0.007%. The differences are caused by the result of an Assessment Ratio.
Assessment Ratio an Assessment ratio is an important variant that affect the property value assessment in many countries such as, Indonesia, the Philippines, and England. When multiply the assessment ratio with the tax base value then a result will become an Assessed Value, for instance; Indonesia indicate their assessment ratio at 40%, if the land and construction value combines to 1 million baht then the Assessed Value will be 400,000 multiplied by nominal rate at 0.5% in which a final tax will be 2,000 baht. This means a property that values 1 million baht; when it is not indicated with the assessment ratio, the tax for that property will be 5,000 baht. However, if there is the assessment ratio for that property, the tax which an owner of the property has to pay is only 2,000 or equal to 0.2% effective rate. The purpose of indicating the assessment ratio in the laws is to make tax becomes more flexible.
Organizations that are responsible for indicating tax ratio Even though the Departments of Local Administration are responsible for the property taxation but the power of indicating the tax ratio is still the duty of the federal government. The study shows that only the Departments of Local Administration of Taiwan and England (only for Council Tax) that have the power to indicate the tax ratio in their areas. Contrary to the Departments of Local Administration in the United States of America and France that the tax ratio indication will be mutually responsible by the State governments or the federal government depends on each case. This is because in these countries, the tax ratio depends on how each local area necessary use a budget.
In Japan, its federal government will be the one responsible for indicating the tax ratio for their local administrations to select and use properly in each area. This goes the same with the Philippines, their federal government indicates the tax ration from in the laws and also with Indonesia that the federal government indicates the tax ratio for their local administrations and gives power to their local administrations to indicate the tax Deduction. And for other countries, the power to indicate the tax ratio is fully in the hands of their federal governments.
Tax collecting Institutions In theory, a duty to collect taxes should be the duty of local administrations because local administrations are more intimate with properties owners and know that whether the owners have use their properties in good use or not.
Most of the countries in the study give full power to the Departments of Local Administration to collect taxes. However, there are some countries that sectors of Ministry of Finance do such work such as, France, Indonesia and Singapore. And for Australia, the country’s State governments will be the ones who collect the taxes because the land tax belongs to the State government.
Tax Receiving It is safe to say that the property tax is an important income for the Departments of Local Administration. Even in some countries the federal government will be the one doing the work but the taxes that the federal government collect will be distribute to local administrations with a proper expense excluded. For Singapore which is a small country, taxes belong to the federal government. On the other hand, South Korea allocates and distributes some of the collected taxes to regional government as well.
Go to 'จับตา' for “เปรียบเทียบการจัดเก็บภาษีที่ดินและสิ่งปลูกสร้าง ของประเทศต่างๆ 10 ประเทศ”
http://tcijthai.com/tcijthainews/view.php?ids=5478
Follow us on TCIJ Facebook Page for more update
www.facebook.com/tcijthai
www.facebook.com/tcijthai
Tags